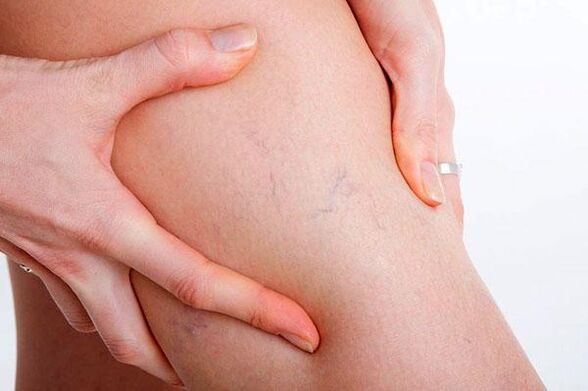
Varicose veins are not only a cosmetic defect that appears in the form of a tree-like blue net on the thighs, legs and upper part of the leg, accompanied by pain and cramps in the lower muscles of the legs, accompanied by a feeling of heaviness when walking or exercising. on the legs. First of all, the risk of thrombosis of the inferior vena cava system is high. It is a serious disease whose symptoms affect every fourth person on the planet.
Thrombotic complications cause the appearance of trophic ulcers on the legs, acute pathologies of blood flow and necrosis of the tissues of the lower extremities. Often, a blood clot that breaks off from the wall of a vessel that enters the circulatory system of the lower extremities ends its journey through the human circulatory system in the heart or brain. A high risk of stroke or heart attack is the main factor in the treatment and prevention of varicose veins, not the unaesthetic appearance of the legs.
Since the onset of the disease, it is constantly developing, affecting new areas of the internal and external venous system of the legs. Therefore, it would be logical to start analyzing the issue with disease prevention. Competent preventive measures in most cases predetermine the speed of development of the pathology that develops against the background of a hereditary defect in the valve apparatus of the venous blood flow of the legs.
Prevention of varicose veins
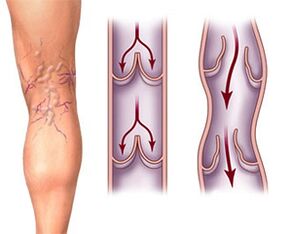
The walls of the veins of the lower extremities are very weak, the muscular system is designed in such a way that it cannot help push the blood through contractions. There are special valves in the veins to control the directional flow of blood and prevent its stagnation. In some people, due to heredity, the valves cannot work properly. However, valve pathology can develop with age:
heavy physical activity;
increased intra-abdominal pressure;
constipation;
frequent pregnancies.
Initially, the process develops in external veins, but as the disease progresses, it affects the deep venous network. The development process of the disease can continue for decades, and the speed depends on the lifestyle, the strength of the blood vessel walls and the intensity of physical activity.
The first task of prevention- to minimize the increase in intra-abdominal pressure, avoid overloading and fight constipation.
The second task- promote the passive outflow of venous blood from the legs. To do this, there is a technique that should be performed better at the end of the day, or even several times during the day. The essence of the technique is to place the stretched legs at an angle of 45 degrees relative to the horizontal. In this case, you need to sleep for at least half an hour. For people who already have varicose veins, it is recommended to sleep with the legs elevated as often as possible.
If you have a disease, you should not use tight shoes and socks with tight elastic bands in order not to complicate the already impaired blood circulation.
Also, when doing sedentary work or just sitting for a long time, you should try to give your feet a horizontal position, if possible, put your feet up. Of course, this does not mean that you should sit with your feet on the table while working in the office. Nope. Just try to put something under the table that allows your legs to rest unobstructed while sitting. You should also avoid the habit of crossing your legs while sitting. You can elevate your feet by placing a few pillows at home.
Conservative treatment
The non-surgical treatment program consists of diet, medication and compression therapy.
Diet
One of the risk factors for the development of varicose veins is excess weight. Therefore, diet is one of the treatment factors. Nutrition should be balanced so that the calories received do not exceed the necessary amount to meet daily needs. Moreover, the number of calories varies depending on whether there is exercise or not. You should also eliminate hot spices, pickles, pepper, excess salt, alcohol, smoked foods from your diet, and eat less fried foods.
The menu should consist of vegetables and fruits with a sufficient amount of vitamin C, high-fiber foods, seafood and wholemeal breads. Frequent small meals are recommended. It should be noted that animal fats should be in moderation. You should not listen to those who say that cholesterol is necessarily evil. A reasonable amount of cholesterol helps to strengthen the vessel walls, reducing the risk of rupture of vessels and repeated thrombotic deposition.
Quit smoking
Smoking is the most harmful habit for varicose veins. The fact is that the tars in the cigarette close the blood vessels, and the carbon dioxide causes vascular spasms. Smoking increases the risk of blood clots, resulting in secondary complications such as heart attacks and strokes. Smoking is especially dangerous for those who have varicose veins and take hormonal drugs.
Compression underwear (socks, socks, knee socks)
This prevention and treatment option is well suited in the early stages of the disease. Underwear can be selected according to several parameters of pressure on soft tissues, color scheme and model selection. Underwear is put on in the morning, before getting out of bed, until the veins are filled with blood. The main obstacle to the use of this method of prevention is the inflated price. Therefore, the main consumers of knitted products are not those who need prevention, but those who use underwear for secondary prevention after surgery.
Varicose veins: drug treatment
Medicines cannot completely cure or stop the disease.
Venotonic - ointments and gels

Venotonics are aimed at strengthening the walls of the vessels, stimulating blood flow and slightly improving microcirculation. These medications, when taken as a course, can reduce pain and swelling. The course of drug use is carried out twice a year and lasts at least two months.
Although ointments and gels are safe, they are practically useless. They cannot penetrate more than the skin and, accordingly, affect the condition of the blood vessels. Ointments and gels are prescribed in the early stages of the disease, when it is not yet known whether it is possible to remove swelling and heaviness in the legs: drugs or postural drainage and the end of physical activity. Sometimes ointment manufacturers are cunning and advise to use the product together with tablets.
Ointment based on flavonoid rutin.
an ointment containing horse chestnut extract is applied twice a day.
gel, the active substance is an extract from grape leaves. There are also capsules of the drug that are taken twice a day on an empty stomach.
Venotonics in tablets
Tablet venotonics are used for varicose veins.
Saponin derivatives of the drug are obtained on the basis of horse chestnut, which contains the bioflavonoid escin plant. These include medicine available in the form of drops and tablets.
The most effective preparations are made on the basis of plant flavonoids obtained from citrus fruits - a strong venotonic. The course of treatment with these drugs can last up to six months.
Rutosides are the first venotonics. Their effect is to improve microcirculation and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Natural rutoside available in tablet and capsule form.
Semi-synthetic rutosides.
Combined rutoside. It combines rutin and a semi-synthetic derivative of ginkgo biloba extract. The drug in the form of capsules is taken twice a day for a month.
Phlebosclerosing drugs
It allows you to remove veins from the bloodstream without surgery. Movement is achieved by the growth of connective tissue that gradually closes the lumen of the vessel. Stimulated by increased coagulation of connective tissue endothelial proteins, as well as irritation of vascular smooth muscles.
An ointment based on acidic sulfur-containing glycosaminoglycan, glucocorticoid and nonionic surfactant is the simplest option. But the effect is so weak that injection solutions are used.
Synthetic phlebosclerotics.
Products containing iodine or based on animal proteins. Medicines are used to selectively close small vessels in the affected areas of the veins. Medicines that do not cause vascular thrombosis are popular among doctors,
 They only burn the walls at the level of the endothelium.
They only burn the walls at the level of the endothelium.
Phlebosclerotic therapy involves injections of drugs or elastic bandages. This is a very simple, painless technique that does not affect the patient's well-being and is quite popular among doctors.
However, isolated sclerotherapy does not provide lasting results and cannot stop the progression of the disease. Therefore, it is better to use it together with surgical treatment. Before therapy, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound examination of the lower extremities to exclude extensive lesions of the saphenous and deep veins.
Contraindications for phlebosclerosis are: drug allergy, atherosclerosis and ischemia of large vessels, obliterating endarteritis, diabetic angiopathy, damage to the blood coagulation system, pregnancy, acute thrombophlebitis of the legs.
Additional medications
Agents that improve blood microcirculation: low molecular weight dextran, purine derivative. These drugs stimulate the breakdown of platelets, reduce blood viscosity and increase the elasticity of red blood cells. These processes improve tissue blood supply and oxidative reactions in them.
Direct or indirect anticoagulants. It reduces the risk of thrombosis. Popular products in the form of ointments and gels have anti-edema, anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic effects.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - suppress inflammatory processes and relieve pain.
Phlebosclerosis therapy options
Before surgery, in the postoperative period, vascular sclerosis is performed to reduce the risk of thrombosis and bleeding.
During surgery as an alternative to vein removal.
Closure of non-operated vessels after surgery.
The puncture method of drug administration is used at any time, and the catheter method is used only during surgery.
Puncture method
In addition to the operating room, it can be performed only in a specialized surgical room, observing all aseptic rules. Large vessels are closed first, then small vessels. Medicines are ordered from top to bottom. The vein is punctured with the patient in an upright position and drugs are administered in a horizontal position. If sclerosis of an enlarged vessel is necessary, the procedure is carried out in several sessions. After the sessions, the patient is registered with a phlebologist for three years for observation.
After applying the drug, the limb is subjected to an elastic bandage, which is repeated for two weeks. In the first week, the bandage is not removed.
The patient should walk within half an hour after the procedure.
The patient should sleep with his limbs elevated every day, avoid sitting and standing for a long time, as well as walking a lot.
Radiofrequency ablation of veins
Vascular ablation using a radiofrequency emitter is a recently emerging field of phlebology. This method allows getting rid of varicose veins painlessly, without complications and with a minimal risk of vessel damage. Radiofrequency radiation affects the inner lining of the vessel wall and destroys it. Thus, the lumen of the vessel collapses and the neighboring tissues are practically not affected. This is a very effective method.
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. Control for accuracy during the procedure is carried out using duplex angioscanning.
After the anesthetic effect, a vein puncture is performed. A catheter with an emitter is inserted into a vein. It progresses to the point where the saphenous vein joins the deep vasculature. With the gradual removal of the catheter, continuous irradiation of the vein from the inside takes place. After the procedure, the puncture site is treated and covered with a bandage. A special elastic sock is placed on the leg. After a half-hour walk under supervision, the patient is allowed to go home. If the patient's work is not related to physical labor, he has the right to work one day after the procedure.
Varicose veinsextensionveins: surgery
The expediency of surgical intervention is reviewed by a phlebologist or vascular surgeon. For women who need surgery to correct a cosmetic defect, doctors suggest postponing the operation if they are planning pregnancy. This is due to the progression of varicose veins during pregnancy and the effect of the operation can be neutralized.
Combined phlebectomy
The most common option for solving the problem of varicose veins using surgery is combined phlebectomy. The operation is performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. All incisions are made as small as possible. For example, the great saphenous vein is removed through a one and a half centimeter incision in the groin. A phlebextractor probe with a special tip is inserted into the vein through the incision. After that, the probe is removed along with the vein. Small veins are removed through small channels called mini-phlebectomy. You should use compression garments after surgery.
Endovasal electrocoagulation
Removal of saphenous veins using current. A more dangerous method compared to radiofrequency obliteration and classical surgery.
Cryosurgery
Removal of veins by exposure to low temperatures. The method is relatively safe. True, the freezing depth is not always accurately calculated, which leads to damage to adjacent tissues or incomplete removal of the vessel.
Intraoperative scleroobliteration
The use of catheter injection of a sclerosing agent into the saphenous veins. Before leg surgery, the saphenous veins of veins and altered areas of veins are noted. During the operation, the anastomosis of the great saphenous vein and femoral vein is opened. The branches of the great saphenous vein are closed. At a distance of 1 centimeter from the femoral vein, the saphenous vein is crossed and ligated. A catheter is inserted into the cut vein, the vein is sutured, and the wound is bandaged. A gauze roll is placed and compressed along the projection of the saphenous vein along the entire length of the leg. A sclerosing substance is injected simultaneously with the removal of the catheter.
Endoscopic dissection
Transillumination phlebectomy of perforating veins allows the veins to be closed and removed from the bloodstream. These vessels connect the subcutaneous network of vessels with the deep network. An endoscopic probe is used.
Laser coagulation
The vein is sealed from the inside with a laser and removed from the bloodstream. It takes a lot of experience to work with highly qualified doctors and lasers.
Treatment of varicose veins at home
At home, varicose veins can be treated with tablets, rubbing ointments, leeches, apple cider vinegar and cabbage leaves. Home treatment can also be done with compression garments or elastic bandages. However, if the disease has progressed, none of the methods will help without surgical treatment.
Today, the only high-quality way to get rid of varicose veins is surgical methods, as well as cases where surgery is combined with sclerotherapy and compression methods.

















